
The main objective of Project BrainGym is to design, develop and evaluate an effective cognitive training therapy based on a brain-computer interface (BCI) system by applying neurofeedback to address cognitive aging. The project has been financed by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, in the call for Strategic Projects Oriented for Ecological Transition and Digital Transition of the State Plan for Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation 2021-2023 (REF: TED2021- 129915B-I00).
The project entitled "Towards the digitization of cognitive aging therapies through brain-computer interfaces, physical training and neuropsychological self-assessment (BrainGYM)" proposes an integrative digital solution to slow cognitive decline associated with normal aging. The project identifies three limitations of current interventions: ineffective cognitive training strategies, subjective assessment of cognitive status, and scalability of current interventions. The project aims to develop a digital intervention that combines brain-computer interfaces (BCI), physical training and neuropsychological self-assessment to address these limitations. In this project we propose the use of neurofeedback techniques to facilitate endogenous stimulation of specific neural circuits using feedback provided by a BCI system, physical exercise to promote the release of neurotrophic factors, and cognitive self-assessment to complement traditional test batteries. The proposed digital intervention is intended to be effective, integrative and scalable in the fight against cognitive aging.
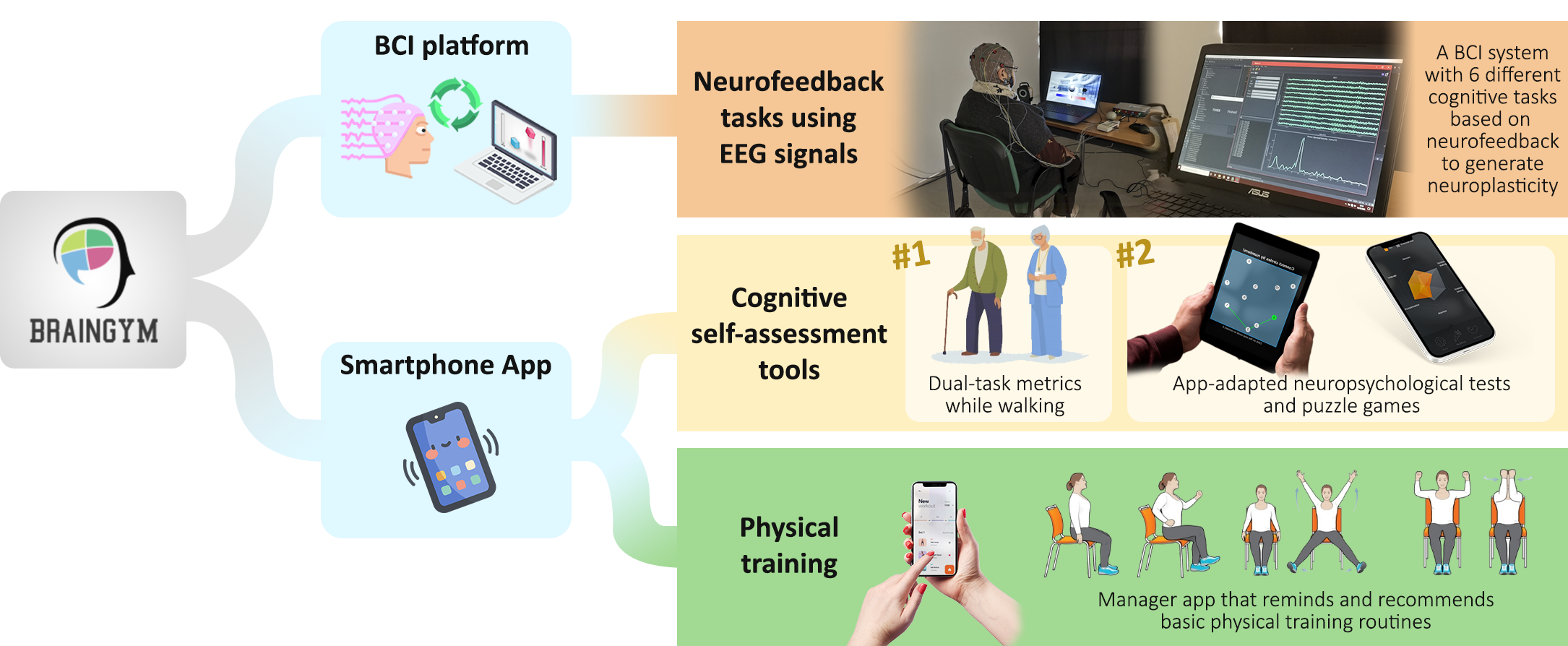
The cognitive training program will be based on state-of-the-art neurofeedback techniques, which allow self-regulation of brain activity through a BCI system to improve neuronal function. Our hypothesis is that this training is more effective than the usual cognitive stimulation therapies.
The physical training program designed by a specialist will consist of monitored sessions and exercise suggestions. These therapies have proven effective in slowing cognitive decline due to improved cerebrovascular function and production of neurotrophic factors.
A comprehensive cognitive assessment is crucial to verify the effectiveness of the training program. In this project, this will be done through the application of neuropsychological tests and the identification of physiological biomarkers derived from the analysis of brain activity.
The Biomedical Engineering Group of the University of Valladolid is a research group of the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Bioingeniería, Biomateriales y Nanomedicina (CIBER-BBN), Consolidated Research Unit (UIC-060) of the Junta de Castilla y León and Recognized Research Group (GIR) of the University of Valladolid. It is mainly formed by Engineers and Doctors from different specialties, who work together in several lines of research, such as brain signal processing as an aid in the diagnosis of different neurological diseases and in the development of non-invasive brain-computer interface (BCI) systems. Their role in the project lies in the development of the BCI system that will allow the application of neurofeedback techniques for the rehabilitation of the cognitive functions of participants. .
Contact - Dr. Roberto HorneroThe City Council of Valladolid, through its Center for the Care of Elderly and Dependent People, manages 12 Active Life Centers that offer services, activities and programs aimed at promoting the prevention of dependency and active and healthy aging, as well as access to social resources, healthy living habits, cultural assets and enriching leisure and free time. It also seeks to encourage active and democratic participation of the elderly, community integration, intergenerational relations, tolerance, mutual aid and volunteering, personal and group development and access to information.
Contact - Servicio de Iniciativas SocialesThe different work packages (WP) associated with the project are shown below:

The BrainGym platform will be designed cooperatively between neuropsychologists and engineers. Suggestions from participants will also be taken into account to increase user motivation. The final design of the tasks will include a detailed description of the visual sequence, the functions to be trained, implementation details, etc.
The implementation of the signal acquisition and processing and the designed tasks will be performed in parallel. The cross-platform mobile application will also be implemented in this task. Finally, a test of the whole platform with the researchers will allow the team to find and correct possible errors before starting the validation with the target users.
At least 90 healthy participants between 65 and 75 years of age will be recruited through the Valladolid City Council. A random subdivision will then be made into control, training and placebo groups.
The characterization of users' cognitive functions will be performed 4 times: before training, just after training, 1 month after and 3 months after. The characterization is composed of a battery of neuropsychological tests, baseline EEG recordings and smartphone assessment.
The 10 cognitive aging training sessions differ according to the subgroup to which the user belongs: traditional occupational therapy (control group), BCI-based training with real NF (training group) or with simulated NF (placebo group). All participants will undergo the physical training program and cognitive self-assessment sessions
The effectiveness of the training program in slowing the effects of cognitive aging will be evaluated by comparing groups at different time points. The results will be disseminated in scientific forums (e.g., research journals, conferences, etc.) and to the general public (e.g., website, media, etc.).