The aim of this project is the development of a bioinformatics tool to assist the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, allowing an early detection and a better characterization of the different Alzheimer stages. This tool will combine genetic data of buccal mucosa samples and brain activity (electroencephalographic recordings). The project has been approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Porto (Portugal). The AD-EEGWA project is co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the Interreg V-A Spain-Portugal Program (POCTEP) 2014-2020.

The Institute of Molecular Pathology and Immunology (IPATIMUP) of the University of Porto was founded in 1989 and has consolidated a position as an international reference in disease research. IPATIMUP research is focused on the study of biological mechanisms of complex diseases, early diagnosis methods, decreasing the incidence of different diseases, increasing treatment effectiveness and, consequently, improving the quality of life of the patients.
Nádia Pinto – npinto@ipatimup.ptThe Biomedical Engineering Group of the University of Valladolid is a multidisciplinary group, mainly formed by Telecommunication Engineers and Doctors of different specialties (pneumology, neurology, psychiatry, neurophysiology, and ophthalmology). Its members have a wide experience in brain signal processing to help the diagnosis of different neurological diseases.
Roberto Hornero – roberto.hornero@tel.uva.esThe Alzheimer Association of Zamora aims to increase the quality of life of people affected by dementia, as well as their families. Since its foundation in 1996, the Association has experienced a continuous growth, currently owning two centres specialized in dementia care, numerous assistance programs and an adapted transport service.
Manuel Figueruelo – direccion@alzheimerzamora.comThe Alzheimer Association of Portugal (North branch) has a wide experience dealing with relatives and patients with Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. This centre has staff with the necessary skills to properly attend Alzheimer's disease patients, along with family members and caregivers; such as a clinical psychologist specialized on geronto-psychology and an occupational therapist with wide experience on people affected by dementia.
Ana Taborda – anasofiataborda@gmail.com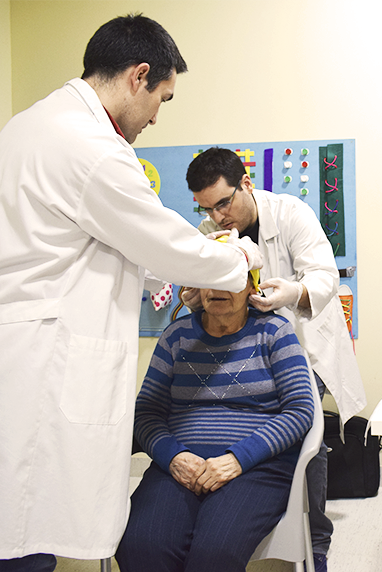
Selection of the sample that will participate in the study (250 subjects taken from both areas of project intervention, divided as follows: 150 patients with Alzheimer's disease at mild, moderate and severe stages, 50 subjects with mild cognitive impairment and 50 controls), plus a collection of their biological samples (buccal mucosa) and their brain activity (electroencephalogram, EEG).
Obtaining the genetic profiles of the participants from the biological material collected in the previous activity, and analysis of the EEG recordings by means of advanced signal processing methods.
Pattern identification by means of meta-analysis, providing assistance in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. This will be carried out combining EEG signals and genetic data from all the participants in the study.
Design of a tool to help in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, based on the analysis carried out in the previous activities. Additionally, we will evaluate the possible exploitation of the aforementioned tool.
Coordination and supervision of each activity by the main beneficiary, each institution being responsible for their own actions.
Participation in conferences to present the preliminary results of the project to the scientific community, publication of papers showing the final results in prestigious international journals, and preparation of communication material to make society aware of the progress of the project (website, social networks, preparation of seminars and press releases).