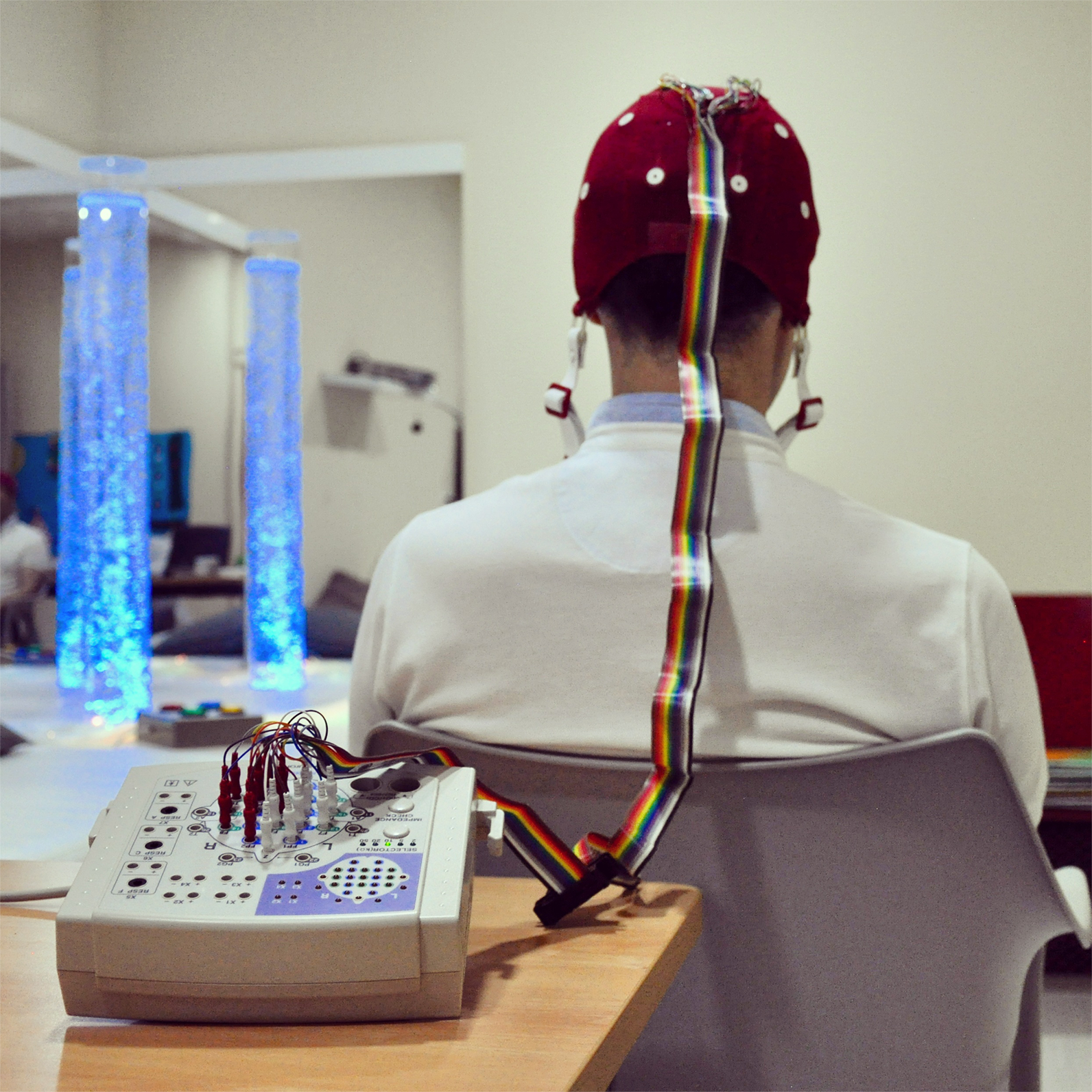
Analysis of neural signals
Oscillatory neural activity reflects the functional brain architecture in real time. Different pathologies, such as Alzheimer Disease, mild cognitive impairment or schizophrenia, modify brain dynamics. This research line is focused on exploring the alterations in the neural activity associated to the previous pathologies, with a threefold purpose:
In order to accomplish these aims, electroencephalographic (EEG) and magnetoencephalographic (MEG) signals are analyzed by means of different advanced signal processing techniques: spectral and nonlinear methods, neural coupling measures and parameters from complex network theory.
Watch related videos
Within the framework of this line of research are the following projects:
Analysis of polysomnographic signals
Polysomnography is the main source of information to investigate sleep. The automatic analysis of nocturnal cardiorespiratory signals is a very useful approach to detect illnesses such as Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome (SAHS) as well as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). The GIB has developed methods to help in their diagnosis by conducting:
Our research is focused on both adult and children patients. Moreover, we are encouraged in the promotion of interdisciplinary national partnerships in Spain (Hospital Universitario Rio Hortega, Hospital Universitario de Burgos) as well as international collaborations (Charité Universitatsmedizin Berlin, Pritzker School of Medicine of the University of Chicago).
Watch related videos
Within the framework of this line of research, three research projects are currently being developed:
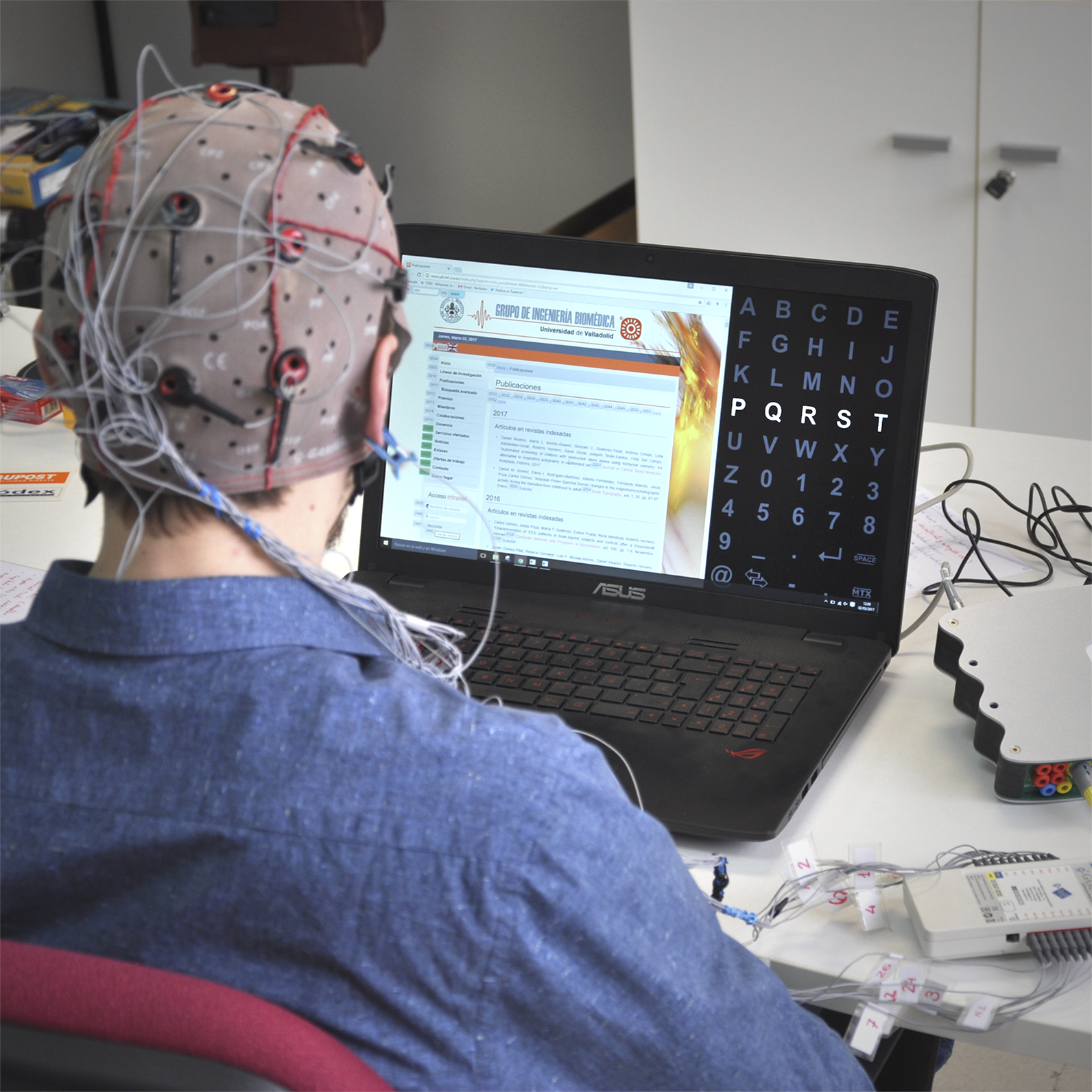

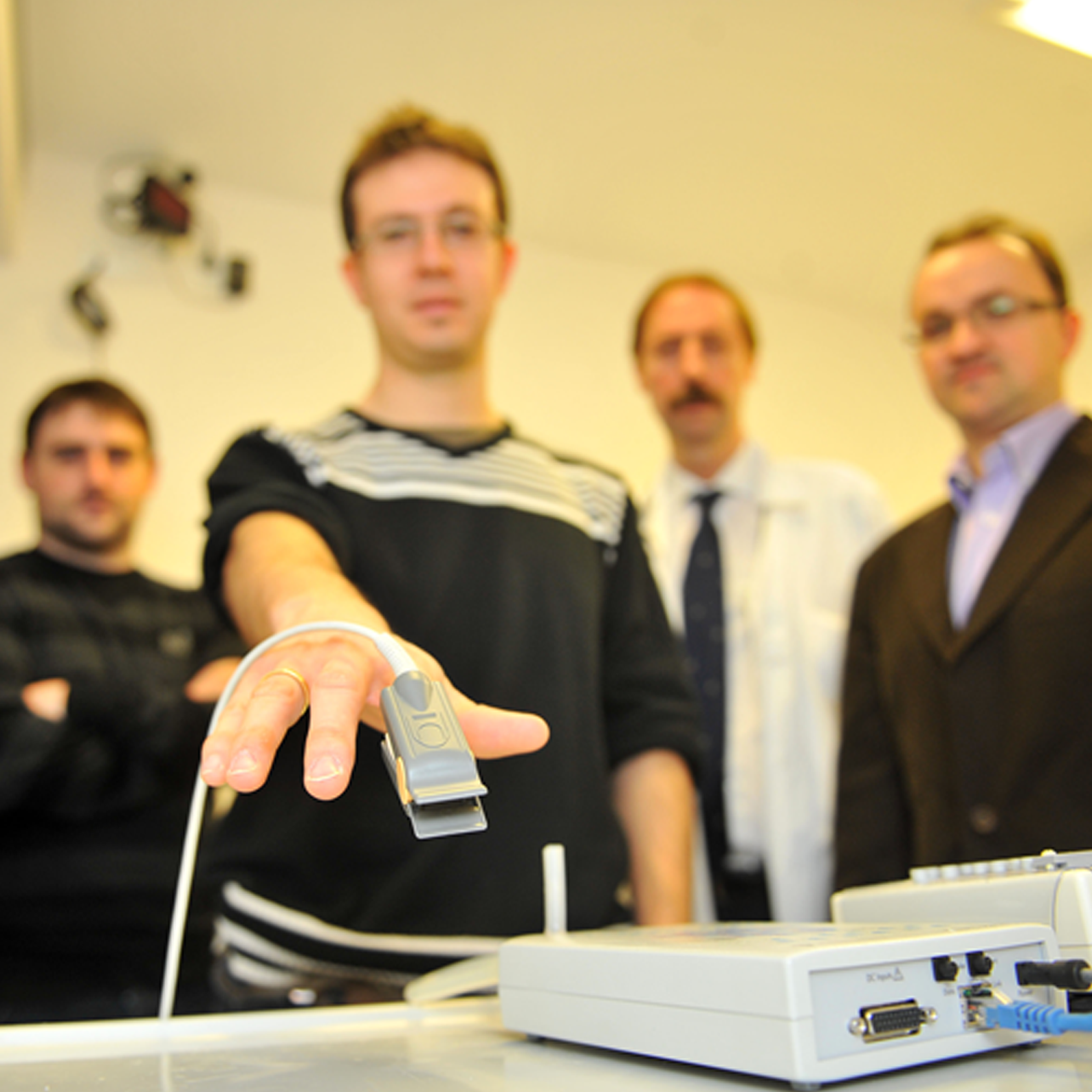
Brain-Computer Interface systems
Brain-Computer Interface systems (BCI) allow users to control applications using their own brain signals.
Design, development and evaluation of asistive applicationsThe main motivation of the BCI systems is focused on increasing the quality of life of those who have a motor disability that limits their ability to communicate by developing asistive applications. In fact, the Biomedical Engineering Group have developed the following projects:
Real-time EEG signal processing
It is also important to develop and test new real-time signal processing methodologies that favor the generalization and the performance of these systems.
Watch related videos
Within the framework of this line of research, the following project has been developed:
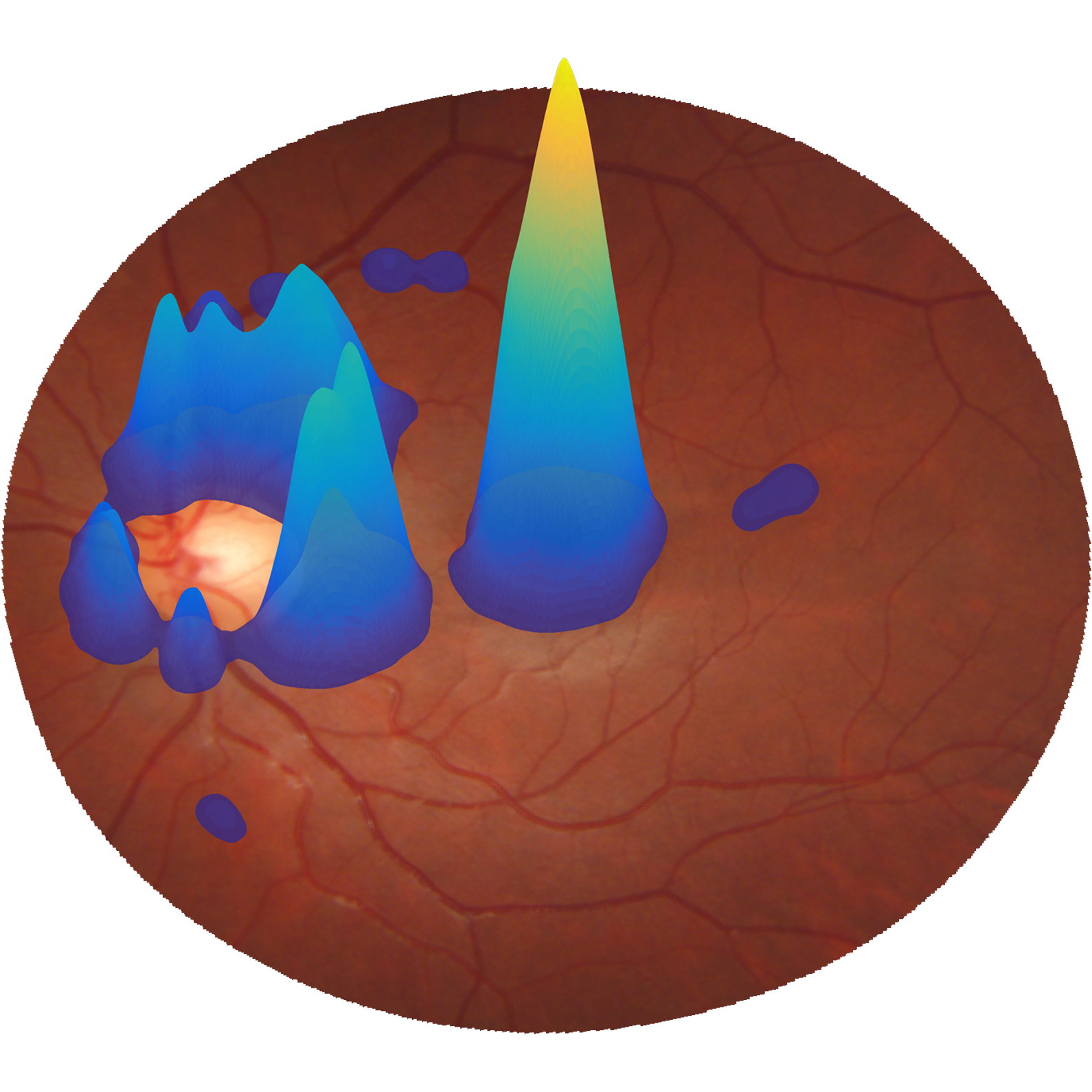
Analysis of retinal images
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a visual complication of diabetes and has become an important cause of blindness in industrialised countries. Early diagnosis is paramount to avoid a severe vision loss, but requires patients to undergo regular eye examinations in which digital images of the retina are captured. With the growing incidence of diabetes, the development of automatic methods to analyse these images could be an important aid in the diagnosis of DR. To achieve this goal, the Biomedical Engineering Group is involved in the following projects:
Within the framework of this line of research, the following project has been developed:
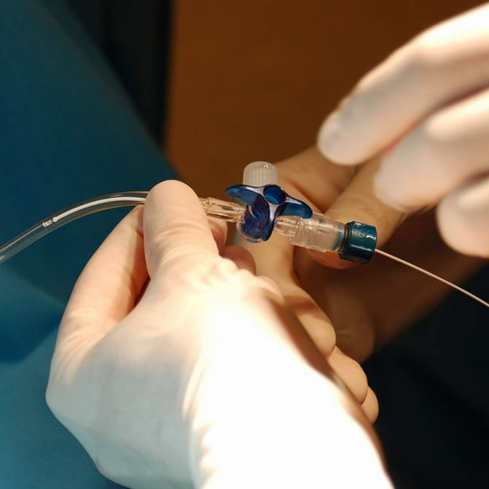
Analysis of intracranial pressure signals
Hydrocephalus is characterised by clinical symptoms, ventriculomegaly and disorders in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulation. Infusion tests are routinely used to study CSF dynamics in patients with hydrocephalus. In them, intracranial pressure (ICP) is artificially raised by the injection of fluid in the lumbar CSF space and the resulting pressure is motorized. Infusion tests can be helpful in the decision about the surgical implantation of a CSF shunt in patients with hydrocephalus. However, they are also useful to study cerebral haemodynamics. In the Biomedical Engineering Group, ICP signals recorded during infusion tests are being analysed with two main objectives:



